
Quota sampling is a non-probability sampling method used in research to ensure that specific subgroups are represented in a study. Researchers set quotas based on characteristics such as age, gender, income, or education level and then collect data from participants who meet those criteria. This research guide explores what Stratified non-random sampling is and when to use it, the step-by-step process for implementing it, its key advantages and limitations, and how AI-powered tools like Eureka enhance sampling research.
Whether you are conducting market research, social science studies, or healthcare surveys, quota sampling provides an efficient, cost-effective way to collect targeted data.
What is Quota Sampling?
What is quota sampling? Eureka Technical Q&A explains its method, advantages, and applications in market research, helping you understand how it ensures representative data collection.
Definition and Key Concept
Quota sampling is a non-probability sampling method where the researcher defines specific subgroups and ensures proportional representation by selecting participants who meet those criteria. This method is particularly useful when time constraints or resource limitations prevent the use of random sampling.
Example: A company conducting a customer satisfaction survey might ensure that 50% of respondents are women and 50% are men to reflect the gender composition of their customer base.
When to Use Quota Sampling
Quota sampling is most effective when:
- Random sampling is impractical due to time or cost constraints
- A representative sample is needed for different subgroups
- Research requires real-time data collection for fast decision-making
- The population of interest is diverse, and subgroups must be proportionally included
Example: In political polling, researchers use quota sampling to ensure data collection reflects different demographics, such as race, income, or geographic region, to predict election outcomes.
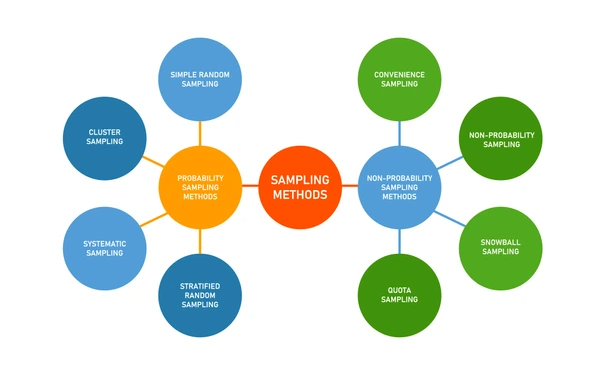
Steps to Implement Quota Sampling
Step 1: Define the Population and Research Objective
- Identify the target population (e.g., “working professionals in New York”)
- Establish the research goal (e.g., “analyzing job satisfaction levels among employees in the finance sector”)
Step 2: Identify Key Subgroups and Set Quotas
- Determine the characteristics that need representation (e.g., age, income, gender)
- Define quotas based on real-world data or past research
Example: If a survey targets 1,000 professionals and 60% of them are male while 40% are female, the quotas should match this proportion.
Step 3: Select Participants Based on Quotas
- Use non-random selection methods such as online surveys, face-to-face interviews, or phone calls
- Continue data collection until each quota is filled
Example: A retail company conducting customer research might survey 200 respondents with quotas ensuring equal representation from different income levels.
Step 4: Analyze and Validate Data
- Ensure proportional representation of all subgroups
- Cross-check quota completion to minimize sampling bias
- Apply statistical weighting if necessary
Example: A healthcare study on vaccine adoption may analyze data to ensure all racial and ethnic groups are proportionally represented.
Advantages of Quota Sampling
- Efficiency – Faster and more cost-effective than random sampling
- Ensures Representation – Guarantees the inclusion of key subgroups
- Flexible – Can be easily implemented across different research fields
Example: A smartphone manufacturer launching a new device can use Stratified non-random sampling to gather insights from different age groups quickly.
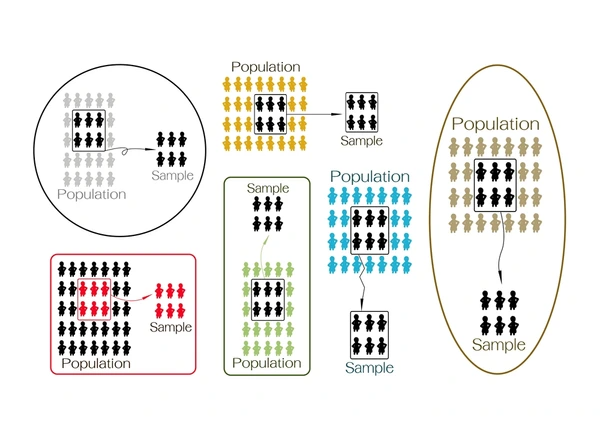
Limitations of Quota Sampling
- Selection Bias – Since participants are not chosen randomly, the sample may not be fully representative
- Non-Generalizability – Findings may not accurately reflect the broader population
- Data Reliability Issues – Researchers might select respondents based on convenience rather than scientific rigor
Example: If a luxury brand surveys only urban customers, the data may not reflect rural consumers’ purchasing behavior.
How Eureka Enhances Quota Sampling Research
What is Eureka?
Eureka by PatSnap is an AI-powered research intelligence tool that helps researchers refine their sampling techniques, analyze large datasets, and ensure accurate representation of target populations.
How Eureka Supports Quota Sampling
- Automated Data Validation – Ensures quota completion accuracy
- Pattern Recognition – Identifies potential biases in sample selection
- Competitive Market Analysis – Optimizes survey designs for better insights
Example of Eureka in Action:
A market research firm using non-probability sampling for product testing can leverage Eureka to analyze consumer trends, track demographic shifts, and refine survey designs for better accuracy.
Conclusion
non-probability sampling is a practical and efficient method for gathering data when random sampling is not feasible. By ensuring proportional representation of key subgroups, it enhances the accuracy of research findings. However, researchers must be cautious of potential biases and ensure data quality through validation techniques. With AI-driven innovation transforming research methodologies, tools like Eureka by PatSnap empower researchers to optimize Stratified non-random sampling, reduce biases, and enhance data-driven decision-making.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of quota sampling?
Stratified non-random sampling ensures that specific subgroups within a population are proportionally represented in a study.
2. How does quota sampling differ from random sampling?
Unlike random sampling, Stratified non-random sampling uses non-random selection methods to fill pre-defined quotas, making it more efficient but potentially introducing bias.
3. What are common applications of quota sampling?
Stratified non-random sampling is widely used in market research, political polling, healthcare studies, and customer satisfaction surveys.
4. What are the risks of quota sampling?
Potential biases, lack of generalizability, and the risk of data selection based on convenience rather than true representation.
5. How does Eureka improve quota sampling research?
Eureka enhances Stratified non-random sampling by automating data validation, detecting biases, and providing advanced analytics for optimizing sample selection.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Quota Sampling, try Patsnap Eureka.


