
Gluconic acid is a mild organic acid derived from glucose through oxidation. It is naturally present in fruits, honey, and wine and is widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, and industrial sectors. Known for its non-toxic and biodegradable properties, C₆H₁₂O₇ serves as a chelating agent, acidity regulator, and preservative. This article explores its properties, applications, and safety considerations.
What is Gluconic Acid?
Gluconic acid is a six-carbon organic acid with a terminal carboxylic acid group and multiple hydroxyl (-OH) groups. It often appears in aqueous solutions or crystalline form and forms glucono-δ-lactone in solution.
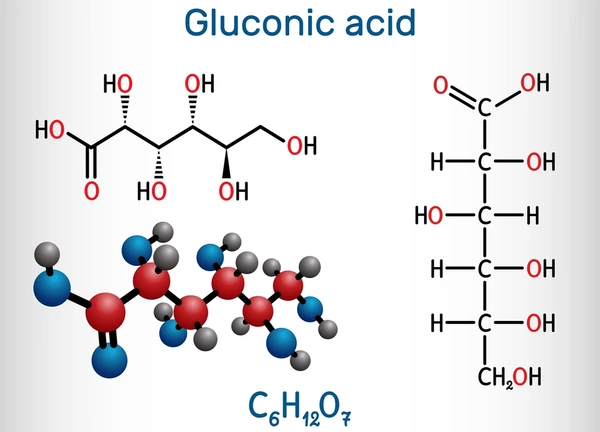
Chemical Properties
- Molecular Formula: C₆H₁₂O₇
- Molar Mass: 196.16 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless crystals or aqueous solution
- Odor: Odorless
- Density: 1.54 g/cm³
- Melting Point: 131°C
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water (316 g/L)
- pH: Approximately 2.1 in a 0.1 M solution
Natural Occurrence and Production
- Naturally found in fruits, wine, and honey due to enzymatic oxidation of glucose.
- Commercially produced via microbial fermentation using Aspergillus niger or other fungi.
- Chemical oxidation of glucose with mild oxidizing agents can also synthesize it.
Applications of Gluconic Acid
Want to learn more about the applications of gluconic acid? Eureka Technical Q&A provides expert insights into its uses in food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and industrial cleaning, helping you understand its benefits and role across various industries.
1. Food Industry
- Acidity Regulator: Adjusts pH in food and beverage formulations.
- Leavening Agent: Reacts with baking soda to produce carbon dioxide for dough rising.
- Preservative: Prevents microbial growth in processed foods.
2. Pharmaceutical and Medical Uses
- Mineral Supplements: Forms salts like calcium gluconate and iron gluconate for treating deficiencies.
- Electrolyte Balancer: Used in intravenous (IV) solutions to regulate mineral levels.
3. Industrial and Chemical Applications
- Chelating Agent: Binds metal ions like calcium, iron, and aluminum, making it useful in cleaning solutions and water treatment.
- Concrete Admixture: Delays the setting time of cement in hot weather conditions, improving workability.
- Metal Surface Treatment: Used in electroplating and corrosion prevention.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Jet Loop Reactor Sika Technology AG | Enhances yield and turnover in enzymatic oxidation of glucose to gluconate, optimizing oxygen levels and enzyme activity. | Industrial-scale gluconate production with reduced energy and material use. |
| Enzymatic Gluconic Acid Production System Genecor, Inc. | Complete conversion of glucose to gluconic acid at concentrations greater than 25% (w/w) ds, resulting in a product essentially free from fermentation impurities. | Production of low-dust dry gluconic acid for food, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications. |
| Antisolvent Crystallization Process Alliance for Sustainable Energy LLC | Effectively recovers glucaric acid and its salts from fermentation broth, achieving high purity with reduced energy consumption. | Sustainable production of glucaric acid for various industrial applications. |
| Zymomonas mobilis Fermentation Process Fujisawa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Achieves high yields of gluconic acid and sorbitol with reduced ethanol production through oxidation-reduction reaction. | Efficient production of gluconic acid and sorbitol for pharmaceutical and food industries. |
| Low pH Stress Gluconic Acid Production Nanjing Forestry University | Yields over 95% gluconic acid from biomass-derived glucose, effectively controlling end-point and decreasing risk of microbial contamination. | Industrial production of gluconic acid from lignocellulosic materials for food, healthcare, and construction industries. |
Safety and Environmental Considerations
1. Toxicity and Human Safety
- Non-toxic and biodegradable, with a 98% degradation rate in two days.
- Recognized as safe (GRAS) by food and health regulatory agencies.
- Skin and Eye Irritation: Concentrated solutions may cause minor irritation, requiring protective gloves and goggles.
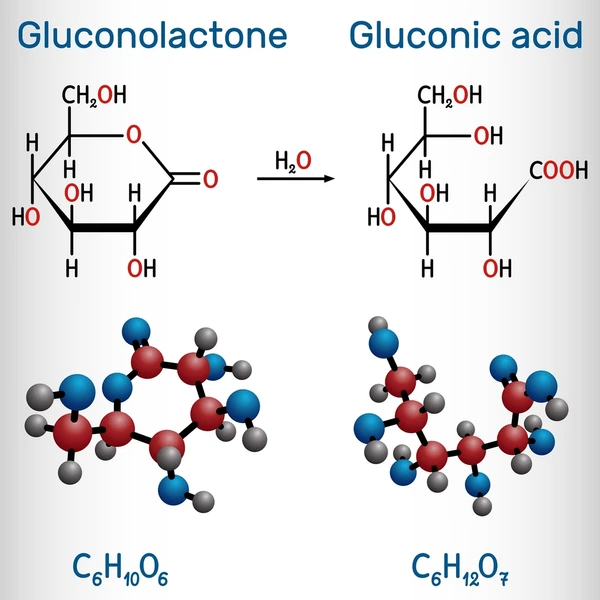
2. Environmental Impact
- Easily biodegradable with minimal ecological risk.
- Safe for wastewater treatment as it does not accumulate in the environment.
FAQs
1. What is gluconic acid used for?
Industries primarily use C₆H₁₂O₇ as an acidity regulator, chelating agent, and preservative in food, pharmaceuticals, and industrial applications.
2. Is C₆H₁₂O₇ safe for consumption?
Yes, C₆H₁₂O₇ is non-toxic and classified as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) by food safety authorities.
3. How is C₆H₁₂O₇ produced?
Microorganisms like Aspergillus niger produce it by fermenting glucose, or manufacturers create it through chemical oxidation.
4. Why is C₆H₁₂O₇ used in cement and construction?
It delays cement setting time, allowing better workability, especially in hot weather.
5. Is C₆H₁₂O₇ an effective cleaning agent?
Yes, its chelating properties help remove metal deposits, scale, and mineral buildup in cleaning and water treatment applications.
Conclusion
Gluconic acid is a versatile, non-toxic, and biodegradable compound with applications in food, medicine, and industrial processing. Its chelating abilities, acidity regulation, and preservative functions make it a valuable additive in multiple industries. With minimal environmental impact and recognized safety, C₆H₁₂O₇ continues to be an essential compound for both commercial and scientific purposes.
To get detailed scientific explanations of gluconic acid, try Patsnap Eureka.


