
Electricity powers the modern world, driving everything from smartphones to power grids. At the heart of electrical systems lies electromotive force (EMF)—the fundamental concept that enables the movement of electrons and the generation of electrical energy. But what exactly is EMF, and why is it so crucial? The answer lies in voltage generation, circuit efficiency, and renewable energy applications. This article explores the science behind EMF, its applications, performance comparisons, and future innovations.
What is EMF?
Electromotive force (EMF) refers to the voltage generated by a source that drives electric current through a circuit. It is measured in volts (V) and represents the energy per unit charge supplied by a power source.
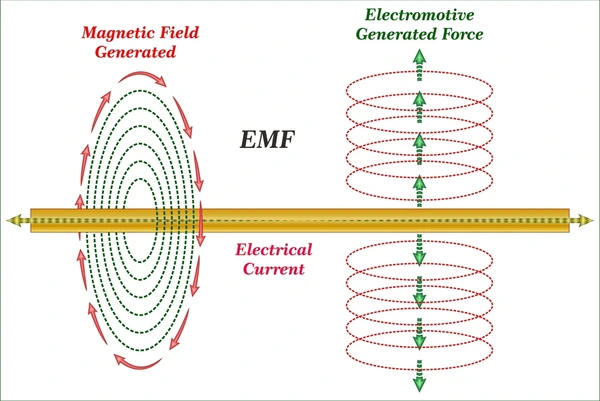
How is EMF Generated?
- Chemical Reactions: Batteries generate EMF through chemical energy conversion.
- Electromagnetic Induction: Generators and alternators use changing magnetic fields to induce EMF.
- Thermoelectric Effects: Heat differentials create EMF in thermocouples.
- Solar Cells: Photovoltaic cells convert light energy into EMF.
💡 Did You Know?
The voltage of a standard AA battery is approximately 1.5V, which is an example of EMF in action.
The Science Behind EMF Generation
Mathematical Representation of EMF
The electromotive force is calculated using the equation:![]()
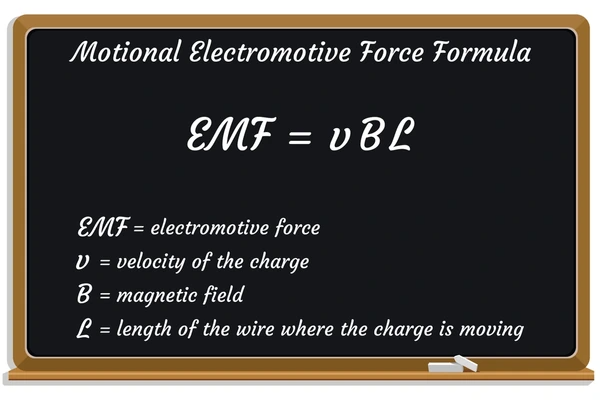
Where:
- V = Terminal voltage
- I = Current in the circuit
- r = Internal resistance of the source
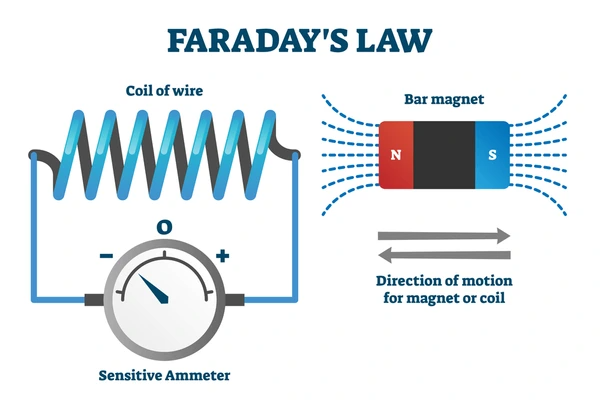
Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction
EMF is also produced when a magnetic field interacts with a conductor. According to Faraday’s Law:EMF=![]()
Where:
- N = Number of coils
- Φ = Magnetic flux
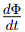 = Rate of change of magnetic flux
= Rate of change of magnetic flux
Why is EMF Important?
- Enables electricity generation in power plants.
- Drives current flow in circuits.
- Powers batteries, solar panels, and generators.
💡 Tip: Higher EMF means stronger voltage output, which improves circuit efficiency.
Performance Comparison: EMF in Different Power Sources
Electromotive force varies depending on the energy source. Here’s a performance comparison:
| Power Source | Typical EMF (V) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Batteries | 1.2V – 12V | Consumer electronics, backup power |
| Solar Cells | 0.5V – 1V per cell | Renewable energy, off-grid power |
| Generators | 110V – 240V | Power plants, industrial applications |
| Thermoelectric Devices | 0.1V – 5V | Sensors, remote power systems |
💡 Did You Know?
A single solar cell generates about 0.6V, but connecting multiple cells increases the voltage to power homes and industries.
Applications of EMF in Different Industries
Electric Power Generation ⚡
- Power stations use steam turbines to generate EMF in alternators.
- Hydroelectric and wind turbines convert mechanical energy into EMF.
Battery Technology 🔋
- Lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries store and deliver EMF for portable electronics and vehicles.
- Rechargeable batteries rely on reversible EMF reactions.
Renewable Energy Systems 🌍
- Solar panels generate EMF from sunlight to power off-grid communities.
- Fuel cells use chemical reactions to generate EMF without emissions.
Medical & Industrial Applications 🏥🏭
- Pacemakers use EMF to regulate heartbeats.
- MRI machines rely on strong electromagnetic fields powered by high-voltage EMF sources.
💡 Curious about how electromotive force (EMF) is applied across industries? Eureka Technical Q&A provides expert insights into its role in electrical power generation, battery technology, and automation, helping you understand its impact on modern energy systems and industrial applications.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| EMF Therapy Device Ivivi Technologies, Inc. | Generates electromagnetic signals with multiple frequency components (0.01 Hz to 100 MHz) satisfying a power SNR model for targeted therapy. | Non-invasive treatment of injuries and diseases in various tissues and organs. |
| EMF-HT Cancer Treatment University of Valencia | Combination of EMFs (25 µT, 4 h) and hyperthermia (52 °C, 40 min) significantly reduces cancer cell viability to 16-50% of control values. | Treatment of various cancer types including melanoma, pancreas carcinoma, and breast carcinoma. |
| Adaptive Hyperthermia System Foundation For Research On Information Technologies In Society | Integrates sensors within antenna elements to measure and correct for mutual coupling and mismatch, achieving precise electromagnetic field excitation and distribution. | Improved hyperthermia treatment for cancer patients, addressing inconsistencies in existing systems. |
| Active EMF Cancellation System Safefields Technologies Ltd. | Actively cancels time-varying magnetic fields using magnetic field generators and sensors, providing efficient and adaptive field reduction. | Reducing EMF exposure in electric vehicle passenger compartments and other enclosed spaces. |
| VLF EMF Measurement Device THE MIND APP LTD | Uses a water-based liquid to simulate human brain interactions, enabling detailed low-frequency EMF analysis. | Assessment and mitigation of EMF pollution, particularly for very low frequency electromagnetic fields. |
Challenges and Limitations of EMF Generation
Although EMF is crucial for electricity generation, it faces some challenges:
Energy Loss in Circuits ❌
- Internal resistance reduces EMF efficiency.
- High-current circuits experience voltage drops.
Battery Limitations ❌
- Chemical degradation lowers battery-generated EMF over time.
- Temperature sensitivity affects battery performance.
Environmental Concerns ❌
- Fossil-fuel-based generators produce EMF but contribute to pollution.
- E-waste disposal is a challenge for battery recycling.
⚠️ Tip: Superconductors and energy-efficient materials improve EMF efficiency!
Future Trends in Electromotive Force Technology
High-Efficiency Batteries 🔹
- Solid-state batteries improve energy density and EMF stability.
Superconducting Generators 🔹
- Reduce energy loss and increase power output in EMF generation.
Wireless EMF Transmission 🔹
- Inductive charging enables wireless energy transfer for electric vehicles and smart devices.
AI-Optimized Power Systems 🔹
- Artificial intelligence (AI) enhances EMF efficiency in power grids and smart grids.
How Eureka by PatSnap Accelerates EMF Innovation
What is Eureka by PatSnap?
Eureka by PatSnap is an AI-powered innovation intelligence tool that helps researchers and engineers discover new breakthroughs in EMF applications.
How It Benefits EMF Research
✅ Patent Analysis: Identifies the latest innovations in battery and generator technology.
✅ Competitive Intelligence: Helps industries benchmark against leading energy companies.
✅ Technology Roadmapping: Provides insights into emerging trends in renewable energy and electrical engineering.
🚀 For researchers and engineers, Eureka by PatSnap accelerates discoveries in EMF-based power systems.
Conclusion
Electromotive force (EMF) is the driving force behind electricity generation, enabling everything from batteries to large-scale power plants. By understanding its principles and improving its efficiency, industries can enhance energy systems and reduce power loss.
With AI-driven tools like Eureka by PatSnap, researchers and engineers can stay ahead of advancements in renewable energy, superconductors, and high-efficiency power sources.
🚀 Want to explore the latest trends in electrical power systems? Sign up for Eureka by PatSnap today and accelerate your innovation journey!
FAQs
1️⃣ What is electromotive force (EMF)?
EMF is the voltage generated by a power source that drives electric current through a circuit.
2️⃣ How is EMF different from voltage?
EMF refers to the total energy supplied per unit charge, while voltage represents potential difference across circuit elements.
3️⃣ What industries rely on EMF?
The energy, automotive, medical, and telecommunications industries utilize EMF for power generation and storage.
4️⃣ Can EMF be increased in a battery?
Yes, by using higher-capacity materials and improving chemical efficiency, EMF in batteries can be enhanced.
5️⃣ How can I stay updated on EMF research?
Using AI-powered tools like Eureka by PatSnap keeps you informed on the latest advancements in electrical power systems.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Electromotive Force, try Patsnap Eureka.


