
Introduction
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) has transformed how we connect audio and video devices by providing seamless transmission of digital signals. Among its features, ARC (Audio Return Channel) and eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel) stand out for simplifying audio connections between TVs and sound systems. While both technologies enable audio transmission over HDMI, eARC offers advanced capabilities, including higher audio quality and greater compatibility with modern formats. In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between HDMI eARC vs. ARC to help you choose the best option for your home entertainment system.

What is HDMI ARC?
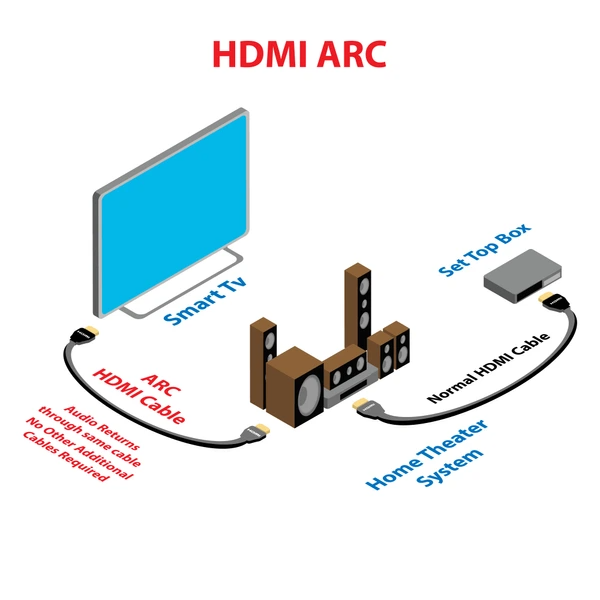
HDMI ARC (Audio Return Channel) is a feature of the HDMI standard that allows two-way audio communication over a single HDMI cable. It enables audio to travel from a display device, like a TV, back to an audio device, such as a soundbar or AV receiver. This eliminates the need for additional cables, simplifying your home entertainment setup and ensuring better audio synchronization.
How HDMI ARC Works
Introduced with the HDMI 1.4 standard in 2009, ARC allows an HDMI connection to act as both an input and output for audio. This feature supports multi-channel audio signals, enhancing the audio-visual experience. Devices like TVs, soundbars, and receivers can seamlessly work together, creating an immersive sound environment.
Benefits of HDMI ARC
- Simplified Setup: Reduces the number of cables needed by combining audio and video in one connection.
- Enhanced Compatibility: Works with many modern devices, including TVs, soundbars, and AV receivers.
- Multi-Channel Support: Handles formats like PCM, Dolby Digital, and DTS for immersive sound experiences.
Limitations of HDMI ARC
- Audio Format Restrictions: ARC supports uncompressed formats but may not handle advanced codecs like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X.
- Downmixing Issues: Some devices may downmix multi-channel audio to stereo, reducing audio quality.
- Bandwidth Constraints: Limited bandwidth can restrict the transmission of high-resolution audio signals.
The Evolution: HDMI eARC
To overcome these limitations, HDMI 2.1 introduced eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel). This advanced feature provides higher bandwidth and supports modern audio formats, including Dolby Atmos and DTS:X. With eARC, users can enjoy full-resolution audio for a more immersive sound experience.
How eARC Works
HDMI eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel) uses two dedicated pins (eARC+ and eARC−) in the HDMI connector for transmitting differential audio signals. This setup allows for bidirectional communication between devices, ensuring seamless audio transfer. Advanced features like clock switching help maintain audio synchronization during transitions, reducing glitches and interruptions.
Applications and Advantages of eARC
- Simplified Setup: eARC allows a single HDMI cable to handle both video and high-quality audio, eliminating the need for extra cables.
- Ideal for Modern Home Theaters: eARC is perfect for setups involving TVs, soundbars, and home theater systems where superior audio quality is a priority.
- Support for Advanced Audio Formats: It supports high-resolution audio formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X, providing a more immersive sound experience.
Compatibility and Requirements
- HDMI 2.1 Port Required: eARC functionality requires an HDMI 2.1 port on both the TV and audio device.
- Cable Compatibility: Not all HDMI cables support eARC. Use a high-speed HDMI cable that can handle the increased bandwidth.
- Device Support: Many modern TVs, soundbars, and AV receivers support eARC, but always check device specifications to ensure compatibility.
eARC vs. ARC: Key Differences
1. Bandwidth and Audio Quality
- eARC: Offers significantly higher bandwidth, supporting up to 32 channels of audio, including 8 channels of 192 kHz, 24-bit uncompressed audio.
- ARC: Limited to compressed audio with a lower bandwidth, supporting up to 6 channels of compressed surround sound.
2. Compatibility
- eARC: Requires devices with HDMI 2.1 ports on both the TV and audio device. Not all devices support eARC, so compatibility checks are essential.
- ARC: Works with devices featuring HDMI 1.4 ports, making it more widely compatible with older systems.
3. Functionality
- eARC: Features its own dedicated data channel, allowing better communication between devices and support for advanced audio formats.
- ARC: Relies on the CEC (Consumer Electronics Control) protocol for device communication, which limits bandwidth and functionality.
4. Use Cases
- eARC: Ideal for high-quality audio setups using advanced formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X in home theaters.
- ARC: Suitable for users who need to transmit stereo or compressed surround sound without the need for advanced audio formats.

eARC vs. ARC: Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between HDMI ARC (Audio Return Channel) and eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel) depends on your audio needs, devices, and future plans.
Why Choose ARC?
- Compatibility: Works with older devices that have HDMI 1.4 or 2.0 ports.
- Basic Audio Needs: Perfect for setups requiring stereo or compressed surround sound.
- Affordability: Ideal for those seeking a cost-effective solution for basic audio transmission.
Why Choose eARC?
- Advanced Audio Quality: Supports uncompressed formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X for a richer audio experience.
- Future-Proofing: Designed for modern devices with HDMI 2.1 compatibility.
- Home Theater Enthusiasts: Perfect for those building advanced setups with immersive sound.
Key Takeaway
If you prioritize high-quality sound and compatibility with advanced audio formats, eARC is the best choice. However, if you’re working with older devices or need a simple, budget-friendly setup, ARC is a reliable option.
Understanding your entertainment needs and equipment capabilities will ensure you select the best option for your home theater system.

FAQs
Can I use eARC with ARC devices?
- eARC is designed to be backward compatible with ARC. However, to fully utilize eARC’s advanced features, both your TV and audio device should support eARC.
Do I need new cables for eARC?
- While standard HDMI cables may work with eARC, it’s recommended to use Ultra High Speed HDMI cables to ensure optimal performance and support for higher data rates.
How can I tell if my devices support eARC?
- Check the HDMI ports on your TV and audio equipment for labels indicating eARC support. Additionally, consult the user manuals or product specifications for confirmation.
Is eARC necessary for Dolby Atmos?
- For Dolby Atmos via Dolby TrueHD (found on Blu-ray discs), eARC is required due to its higher bandwidth capabilities. However, Dolby Atmos through Dolby Digital Plus (used in streaming services) can work with standard ARC.
To get detailed scientific explanations of eARC vs. ARC, try Patsnap Eureka.

