
Overview of Concave and Convex Mirrors
Mirrors are essential tools in both everyday life and scientific applications. Concave vs. convex mirror play crucial roles in shaping light and images. Concave mirrors curve inward, focusing light to a point, while convex mirrors curve outward, spreading light. Each type has unique properties that make it useful in various fields, from optics and astronomy to security and vehicle design. This article will explore the key differences between concave vs. convex mirror, their functions, and their real-world applications.
How Concave Mirrors Work
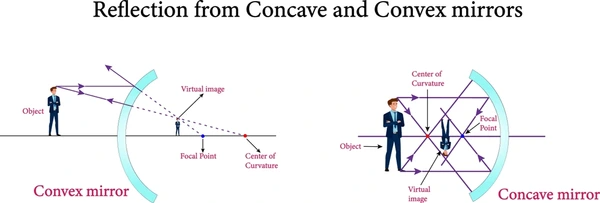
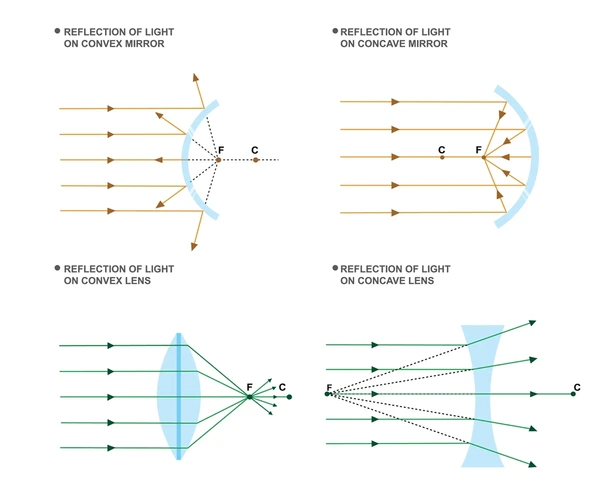
Concave mirrors are curved mirrors that reflect light inward towards a focal point. Unlike convex mirrors, which spread light outward, concave mirrors concentrate it. This unique property makes them useful in many practical applications.
Reflection Principle
Concave mirrors reflect light inward towards their focal point. This is the key feature that differentiates them from convex mirrors, which reflect light outward.
Image Formation
When light rays strike a concave mirror, they converge at a single point called the focal point. This convergence allows the mirror to form real images. These images are inverted and can be projected in front of the mirror at the focal point.
How Convex Mirrors Work
Convex mirrors are curved mirrors that reflect light outward. This causes the reflected rays to diverge, giving them a unique ability to cover a larger field of view. This feature makes them highly useful in various settings, from vehicles to security systems.
Principle of Operation
Convex mirrors curve outward, away from both the light source and the object being reflected. When light hits the mirror’s surface, it reflects at an angle. The reflected rays appear to diverge from a single point behind the mirror, known as the virtual focal point. Although this focal point is imaginary, it helps explain the mirror’s behavior.
Image Formation
The image formed by a convex mirror is always virtual, upright, and diminished (smaller). The light reflects in such a way that it appears to come from behind the mirror. This makes the image appear smaller and farther away than the actual object.
Practical Uses of Concave Mirrors
- Optical Instruments: Concave mirrors are commonly used in telescopes and microscopes. They focus light to create clear images, which is crucial for magnification purposes.
- Vehicle Headlights and Flashlights: The converging property of concave mirrors makes them perfect for vehicle headlights and flashlights. By focusing light into a beam, they significantly improve visibility and illumination.
- Solar Furnaces: Concave mirrors play a key role in solar furnaces. They concentrate sunlight to generate high temperatures, which can be used for applications like cooking, electricity generation, and industrial processes.
- Aerospace: In aviation, concave mirrors are used in aircraft landing systems. They help create clear images of the runway, guiding pilots and ensuring precise landings.
- Security and Surveillance: Concave mirrors, as well as convex varieties, are used in security systems. They provide a wide field of view, helping monitor large areas in stores, offices, and other facilities.
- Augmented Reality Systems: Concave mirrors are being explored for use in augmented reality (AR) systems. Non-reversing magic mirrors can display horizontally flipped images, which are useful in interactive AR applications.
- Tunable Filters: Concave mirrors are used in tunable filters, such as the Fabry-Perot filter. These filters are essential for selecting specific wavelengths of light in various optical applications.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Catadioptric Projection Objectives Carl Zeiss SMT GmbH | Utilizes concave mirrors and optimized mirror groups to achieve high numerical aperture, efficient imaging, and aberration correction while reducing material usage. | Microlithography, especially ultraviolet lithography for semiconductor manufacturing. |
| Catadioptric Reduction Projection Objectives Carl Zeiss SMT GmbH | Compact design with concave mirrors and aspheric lenses enables high-resolution, large-field imaging with reduced material usage and enhanced throughput. | Microlithography systems for semiconductor manufacturing, requiring high-resolution patterning. |
| Fiber-optic Tunable Filters Kyung Hee University System | Concave mirror fabricated on fiber end simplifies cavity alignment and reduces vibration sensitivity, enabling high-speed tuning and high finesse. | Optical communications, spectroscopy, and other applications requiring tunable optical filters. |
| High-speed Multiview Imaging System Duke University | Utilizes concave parabolic or ellipsoidal mirrors and fast scanners to achieve wide angular coverage approaching 4π steradians for 3D imaging and resolution enhancement. | Computational 3D imaging, optical projection tomography, synthetic aperture microscopy, and other techniques requiring multiangle illumination or imaging. |
Practical Uses of Convex Mirrors
Vehicle Rear-View Mirrors: Convex mirrors are commonly used in vehicle rear-view mirrors. Their curved surface allows drivers to see a larger area behind and around the vehicle, enhancing overall safety.
Security and Surveillance: Convex mirrors are essential for security in various settings, such as offices, hospitals, hotels, schools, and stores. They are often installed in hallways, intersections, and blind spots to improve monitoring and prevent accidents.
Parking and Navigation Aids: Convex mirrors play a key role in parking lots and garages. Their wider view helps drivers easily spot obstacles and other vehicles, reducing the risk of accidents and improving parking efficiency.
Road Safety: Convex mirrors significantly improve road safety by offering a broader view of the road and surrounding areas. This wider visibility helps drivers spot hazards early, reducing the likelihood of accidents caused by blind spots.
Industrial and Commercial Applications: Convex mirrors are vital in industrial and commercial settings. In warehouses, factories, and construction sites, they assist in monitoring large equipment and machinery, ensuring safety and operational efficiency.
Fashion and Retail: Convex mirrors enhance the shopping experience in fashion and retail environments. They are used in smart makeup mirrors and virtual fitting rooms, enabling customers to see themselves from multiple angles and try on virtual clothes and accessories.
Panoramic 3D Scanning: They provide a comprehensive view of scanned objects or environments, which is especially useful in applications like interior design, archaeology, and heritage preservation.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Adjustable Mount Assembly The Boeing Co. | Provides a tool-free, secure attachment solution for convex mirrors on cubicle/office partition walls, enhancing visibility and adaptability. | Office spaces, cubicles, and partitions where improved visibility and adaptability are required. |
| Catadioptric Projection Objective Carl Zeiss SMT GmbH | Addresses the challenge of achieving high numerical aperture and reducing material usage, enabling efficient and high-fidelity imaging for immersion lithography. | Semiconductor manufacturing, lithography systems, and applications requiring high-resolution imaging. |
| Magic Mirror System Technische Universität München | Explores the perceptual differences between traditional and non-reversing magic mirrors for screen-based Augmented Reality (AR) systems, with potential applications in anatomy teaching. | Educational and training environments, particularly in the medical field, where AR-based visualization and learning can be beneficial. |
| Projection Optical System Ricoh Co., Ltd. | Addresses the challenge of large-screen projection with reduced distortion and chromatic aberration by using a dioptric and reflecting system to create and magnify intermediate images, achieving efficient and compact image projection. | Large-screen projection applications, such as theaters, auditoriums, and venues requiring high-quality image projection with minimal distortion. |
| Omnidirectional Vision System University of Sao Paulo | Presents the development of an omnidirectional vision system using convex mirrors, providing a 360° field of view for robotic applications such as navigation, teleoperation, and visual servoing. | Robotics, autonomous systems, and applications requiring panoramic vision and situational awareness. |
Conclusion: Which Mirror Is Best for You?
Choosing between concave and convex mirrors depends on your specific needs. If you need magnification and precise image focusing, concave mirrors are ideal, especially for applications like telescopes or vehicle headlights. On the other hand, convex mirrors work best when you need a wider field of view, such as in rear-view mirrors or security systems.
Consider how each mirror type impacts your desired outcome. Concave mirrors are perfect for focused, clear images, while convex mirrors provide a broader, more panoramic view. Ultimately, the right mirror for you will depend on your purpose—whether that’s enhancing detail or increasing visibility over a larger area.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Concave vs. Convex Mirror, try Patsnap Eureka.

