
What is a CBCT Scan Dental?
A CBCT Scan Dental, or Cone Beam Computed Tomography Scan, is a specialized imaging technique used in dentistry to produce three-dimensional (3D) images of the teeth, jawbone, and surrounding tissues.
How Does a CBCT Scan Dental Work?
- X-ray Beam and Detector: During a CBCT scan, a cone-shaped X-ray beam is emitted from an X-ray tube, which rotates around the patient’s head. A digital detector captures the X-ray data as it passes through the patient’s body.
- Data Collection: The detector records hundreds of images at small angular increments as the X-ray source rotates. This data is then used to create a three-dimensional dataset.
- Image Reconstruction: The collected data is reconstructed into a 3D image using specialized software, allowing dentists to view the images from various angles without superimposition of structures.
Key Features of CBCT Scan Dental
- Three-Dimensional Imaging: Provides clear, undistorted views of complex anatomical structures.
- Lower Radiation Dose: Significantly reduces exposure compared to conventional CT scans.
- Detailed Visualization: Allows for precise identification of small details like root canals and bone density.
- Versatility: Can be used for various dental specialties and procedures.
- Improved Treatment Planning: Enhances accuracy and effectiveness of treatment plans.
- Reduced Need for Multiple X-rays: Often provides all necessary information in a single scan.
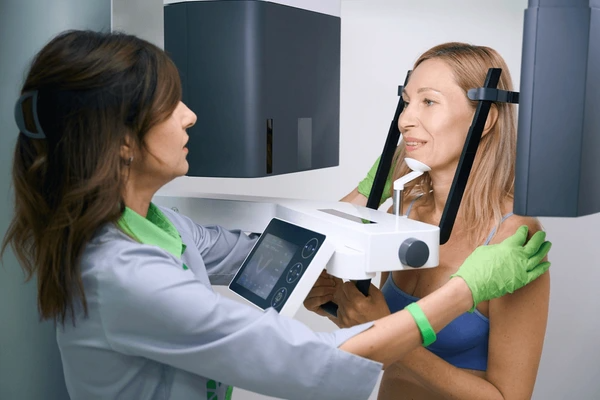

Advantages of CBCT Scan Dental
- High Accuracy: Provides precise 3D images for accurate diagnoses and treatment planning.
- Low Radiation: Delivers lower radiation doses compared to conventional CT scans, reducing patient exposure.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of dental applications, from orthodontics to oral surgery.
- Improved Outcomes: Enhances treatment success rates by providing detailed anatomical information.
Challenges and Limitations
- Radiation Exposure: Although lower than conventional CT scans, CBCT scans still involve ionizing radiation, which can be a concern, especially in pediatric patients.
- Cost: CBCT scanners and scans can be more expensive than conventional imaging techniques.
- Training and Interpretation: Requires specialized training and expertise to interpret the 3D images accurately.
- Indications: Not suitable for all cases, such as extensive fractures involving soft tissue or suspected bone tumors with soft tissue participation, where other imaging modalities like MRI may be preferred.
Legislation and Guidelines for CBCT Use
- Various guidelines have been published to address the safe use of CBCT in dentistry, particularly regarding radiation protection and image interpretation.
- The American Dental Association (ADA) recommends that CBCT images should be evaluated by dentists with appropriate training and education
- Legislation and guidelines aim to balance the benefits of CBCT with the potential risks, emphasizing the need for proper training and adherence to safety protocols.
Comparison with Conventional Imaging Techniques
- Image Quality: CBCT provides higher-resolution images with better detail, especially in three dimensions, compared to conventional 2D X-rays.
- Radiation Exposure: Significantly lower radiation dose compared to medical CT scans, making it safer for patients.
- Diagnostic Confidence: The 3D images obtained from CBCT enhance diagnostic confidence and treatment planning accuracy.
- Versatility: CBCT can be used for a broader range of applications, including those requiring detailed bone and soft tissue analysis.
Applications of CBCT Scan Dental
Dental Implant Planning
CBCT is extensively used for planning dental implant placements due to its ability to provide high-resolution, three-dimensional images of the jawbone and surrounding structures. It helps in assessing bone density, identifying suitable implant sites, and planning the optimal position for implants.
Orthodontic Diagnosis and Treatment
In orthodontics, CBCT is valuable for detailed assessments of dental and skeletal structures. It allows for precise measurements and evaluations that are crucial for treatment planning, particularly in cases involving complex malocclusions or orthognathic surgery.
Endodontic Procedures
CBCT is useful in endodontics for diagnosing and treating root canal issues. It provides detailed images of the root structures, helping in the identification of fractures, resorptions, and other anomalies that may affect treatment outcomes.
Periodontal Evaluation
For periodontal diseases, CBCT helps in evaluating bone loss, furcation involvement, and other periodontal defects with high accuracy. It offers a more comprehensive view compared to conventional radiographs, aiding in better diagnosis and treatment planning.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Assessment
CBCT is used to evaluate the TMJ and surrounding structures, providing detailed images that are essential for diagnosing and treating TMJ disorders.
Restorative Dentistry
In restorative dentistry, CBCT is used for creating detailed images of teeth and surrounding tissues, which are crucial for planning crowns, bridges, and other restorative procedures.
Forensic Dentistry
CBCT is employed in forensic dentistry for age estimation and identification purposes, particularly in cases involving dental age assessment.
Surgical Guidance
CBCT provides three-dimensional images that are essential for surgical planning and guidance in oral surgery, helping in minimizing risks and improving surgical outcomes.

Latest Technical Innovations in CBCT Scan Dental
X-ray Tube and Detector Technology
- Advances in X-ray tube design, such as the use of a nominal focal spot of 0.5 mm operating at 70–100 kVp and 1–4 mA, improve image quality and reduce radiation dose.
- The integration of digital CCD cameras with image intensifiers enhances detector technology, allowing for higher resolution and faster imaging times.
Adaptive Exposure Techniques and Beam Geometry
- Implementing adaptive exposure techniques adjusts radiation dose based on patient size and anatomy, optimizing image quality while minimizing exposure.
- Innovations in beam and rotation geometry aim to reduce scatter radiation and improve image accuracy.
Reconstruction Algorithms and Image Processing
- Advanced reconstruction algorithms deliver high-quality images with improved modulation transfer function (MTF), noise reduction, and geometric accuracy.
- Metal artifact reduction (MAR) techniques are being developed to mitigate the effects of metal-induced imaging artifacts, enhancing the diagnostic accuracy of CBCT scans.
Integration with Other Technologies
- The combination of CBCT with optical imaging and dual-energy CT (DECT) systems is being explored to reduce metal artifacts and improve image quality.
- Virtual monoenergetic images (VMI) synthesized from DECT datasets help in reducing metal artifacts, particularly for small metallic objects like dental implants.
Portable and Cost-Effective Solutions
- The development of smaller, lighter CBCT scanners with a cone-like beam design makes them more portable and affordable for dental practices, allowing for easier positioning and movement to image different parts of the dental arch.
- These scanners maintain low radiation doses and fast imaging times, making them suitable for various dental applications.
To get detailed scientific explanations of cbct scan dental, try Patsnap Eureka.

