
Atomic physics has revolutionized our understanding of the microscopic world, shaping modern science and technology. One of the fundamental concepts in quantum mechanics is the Bohr radius (a₀), which defines the most probable distance between the nucleus and an electron in a hydrogen atom. But why is the a₀ significant? The answer lies in atomic structure, quantum mechanics, and applications in nanotechnology. This article explores the science behind the Bohr radius, its importance in quantum theory, and its role in modern research and technology.
What is the Bohr Radius?
The Bohr radius (a₀) is a physical constant that represents the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus in a hydrogen atom in its ground state. It was introduced by Niels Bohr in his quantum model of the atom.

Key Properties
- Symbol: a₀
- Value: 5.29177 × 10⁻¹¹ meters (or 0.529 Ångströms)
- Relation to Quantum Mechanics: Forms the foundation of the Bohr model
- Significance: Determines atomic structure and energy levels
💡 Did You Know?
The a₀ is not a fixed boundary but a probabilistic measure that represents where an electron is most likely to be found around a nucleus.
The Science Behind the Bohr Radius
The a₀ is derived using quantum mechanics and fundamental physical constants.
Formula
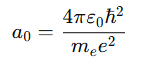
Where: 
This formula connects classical physics with quantum theory, demonstrating how electrons behave under the influence of Coulomb’s force and angular momentum quantization.
Why is the Bohr Radius Important?
- Defines electron orbits in hydrogen-like atoms
- Establishes atomic energy levels
- Provides a benchmark for atomic scale measurements
💡 Tip: The Bohr radius is only valid in the Bohr model, but remains useful in more advanced quantum mechanics.
How the Bohr Radius Affects Atomic Structure
The a₀ plays a crucial role in determining atomic sizes and interactions. Here’s how it influences atomic behavior:
- Electron Distribution: Defines the size of electron orbitals in hydrogen-like atoms.
- Energy Levels: Helps calculate electron energy states using the Bohr model.
- Quantum Transitions: Determines wavelengths of emitted photons during energy level transitions.
Comparison of Atomic Radii Based on Electron Configuration
| Atom | Bohr Radius Equivalent (Å) | Atomic Radius (Å) |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 0.529 | 0.53 |
| Helium (He) | 0.313 | 0.31 |
| Lithium (Li) | 1.45 | 1.52 |
| Carbon (C) | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| Oxygen (O) | 0.65 | 0.66 |
💡 Did You Know?
The Bohr radius is smaller than the atomic radius because electron interactions modify the simple hydrogen-like structure.
Applications of the Bohr Radius in Different Fields
Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Physics ⚛️
- Forms the foundation of Schrödinger’s wave equation
- Used in atomic orbital calculations and energy level predictions
Nanotechnology and Semiconductor Physics 💻
- Determines the size of quantum dots and nanoparticles
- Influences electronic behavior in semiconductors
Spectroscopy and Astrophysics 🌌
- Helps explain atomic emission spectra in stars
- Used in determining interstellar element compositions
Theoretical and Experimental Research 🔬
- Integral to quantum electrodynamics (QED)
- Supports experimental atomic physics studies
Challenges and Limitations
While the a₀ is a crucial concept, it has some limitations:
Bohr Model Approximation ❌
- Only accurately describes hydrogen-like atoms
- Does not account for electron-electron interactions in multi-electron atoms
Quantum Mechanical Complexity ❌
- The Schrödinger equation provides a more accurate atomic model
- Real atoms do not have fixed orbits but probabilistic electron clouds
Relativistic Effects ❌
- The Bohr model ignores relativistic corrections required for high-speed electrons
⚠️ Tip: The a₀ remains a useful approximation but should be understood within the limits of classical quantum models.
Wondering how the Bohr radius applies across different fields? Eureka Technical Q&A provides expert insights into its role in quantum mechanics, atomic structure, and nanotechnology, helping you understand its significance in both theoretical and applied sciences.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Gravitational Atom Model Amherst College | Proposes a revised gravitational Bohr radius on the order of 2πa₀, based on a discrete fractal cosmological paradigm. | Theoretical cosmology and gravitational physics at atomic scales. |
| Quaternionic Function Analysis Tool Hefei University of Technology | Generalizes Bohr radius for slice regular functions over quaternions, extending complex analysis techniques. | Non-commutative analysis and quaternionic function theory. |
| TMDC Exciton Modeling System Tianjin University | Corrects exciton Bohr radius in monolayer TMDCs, accounting for exciton-optical phonon coupling effects. | Nanoelectronics and optoelectronic devices using 2D materials. |
Future Trends in Quantum Research and the Bohr Radius
Quantum Computing and Atomic Precision 🔹
- Bohr radius influences quantum dot design for quantum processors
Nanomaterial Science and Atomic Engineering 🔹
- Determines electron confinement effects in nanomaterials
High-Energy Physics and Theoretical Models 🔹
- Used in testing fundamental physical constants
How Eureka by PatSnap Accelerates Quantum Research
What is Eureka by PatSnap?
Eureka by PatSnap is an AI-powered innovation intelligence tool that helps R&D teams explore advancements in atomic physics, quantum mechanics, and nanotechnology.
How It Benefits Bohr Radius Research
✅ Patent Analysis: Identifies cutting-edge patents in atomic and quantum physics.
✅ Competitive Intelligence: Helps research teams benchmark against global advancements.
✅ Technology Roadmapping: Tracks emerging trends in quantum mechanics and nanoscience.
🚀 For physicists, researchers, and technology innovators, Eureka by PatSnap accelerates research and fosters groundbreaking discoveries.
Conclusion
The Bohr radius remains a fundamental concept in atomic physics, defining electron orbits, energy levels, and quantum mechanical behavior. While modern quantum mechanics provides more sophisticated models, the a₀ continues to influence research in nanotechnology, quantum computing, and spectroscopy.
By leveraging AI-driven tools like Eureka by PatSnap, researchers and physicists can stay ahead of scientific advancements and drive new innovations in atomic-scale technology.
🚀 Want to explore the latest discoveries in atomic physics? Sign up for Eureka by PatSnap today and accelerate your innovation journey!
FAQs
1️⃣ What does the Bohr radius represent?
The most probable electron distance from the nucleus in a hydrogen atom.
2️⃣ Is the Bohr radius the same for all elements?
No. Different elements have varying atomic radii due to electron shielding and nuclear charge.
3️⃣ How is the Bohr radius used in quantum mechanics?
It serves as a reference for atomic size calculations and wavefunction modeling.
4️⃣ Why does the Bohr model not fully describe real atoms?
It ignores electron interactions and relativistic effects, making it less accurate for multi-electron atoms.
5️⃣ How can I stay updated on quantum research?
Using AI-powered tools like Eureka by PatSnap helps track the latest patents, innovations, and quantum discoveries.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Bohr Radius, try Patsnap Eureka.


