
What Are Alkaline Earth Metals?
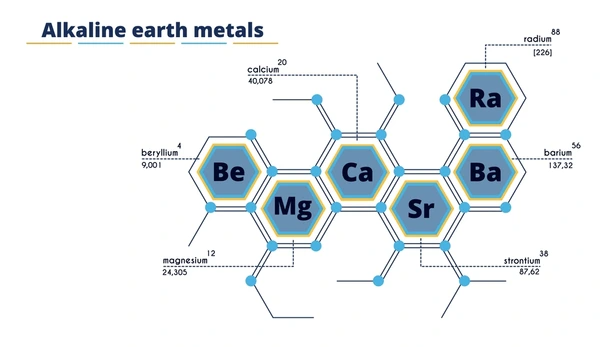
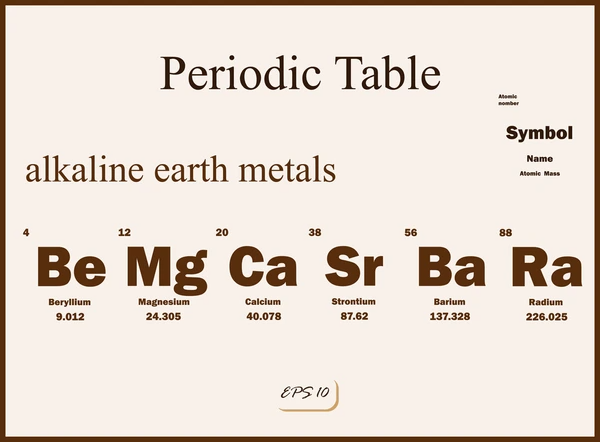
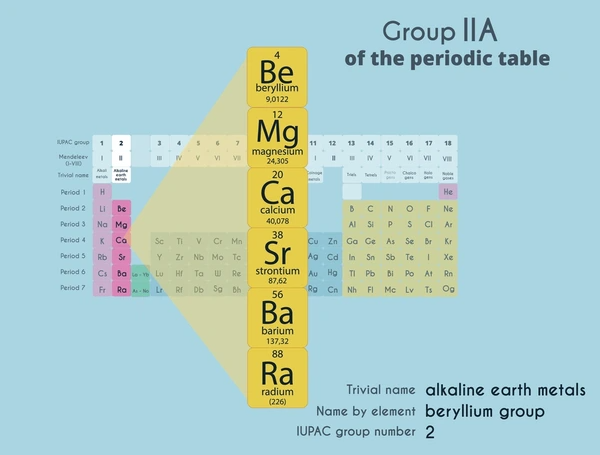
Alkaline earth metals are a group of metallic elements in the second column of the periodic table, which include beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). These elements are characterized by having two valence electrons in their outermost shell, which makes them highly reactive, especially with nonmetals.
Physical Properties
- Malleability and Ductility: Alkaline earth metals are generally malleable and ductile, meaning they can be pounded into thin sheets (malleable) and drawn into wires (ductile).
- Electrical and Thermal Conductivity: These metals exhibit good electrical and thermal conductivity, which means they can efficiently conduct electricity and heat.
- Reactivity: At standard temperature and pressure, alkaline earth metals are less reactive than alkali metals but still react with water and acids to produce hydrogen gas.
- Physical State: Most alkaline earth metals are solids at room temperature, with the exception of mercury (Hg), which is a liquid.
Chemical Properties
- Oxidation States: The most common oxidation state for alkaline earth metals is +2, which is due to the loss of two electrons from their outermost energy level.
- Reactivity with Non-Metals: They react with non-metals such as nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur to form compounds like oxides, nitrides, and sulfides.
- Formation of Salts: They form salts when they react with acids. For example, calcium reacts with hydrochloric acid to form calcium chloride.
- Coordination Chemistry: Alkaline earth metals can form coordination compounds with various ligands, which are useful in catalysis and other applications.
- Thermal Stability: Alkaline earth metal salts, such as those of magnesium and calcium, exhibit good thermal stability and are used in various industrial applications.
Reactivity and Safety
- Reactivity: They are highly reactive with air, water, and acids, which can lead to hazardous situations.
- Handling Precautions: Proper protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, should be worn when handling these metals to avoid skin and eye contact.
- Storage: They should be stored in a dry, cool place under an inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation and moisture absorption.
Comparison with Transition Metals
- Electron Configuration: Transition metals have partially filled d orbitals, allowing them to exhibit a wide range of oxidation states and engage in catalytic and magnetic properties. In contrast, they have fully filled s and p orbitals, leading to more predictable chemical behavior.
- Coordination Chemistry: Transition metals are known for their extensive coordination chemistry, forming complexes with various ligands. While alkaline earth metals can also form coordination compounds, their chemistry is generally less complex and less varied.
Applications of Alkaline Earth Metals
- Industrial Applications: Beryllium (Be) and Magnesium (Mg) are commonly used in industry due to their low density and high strength-to-weight ratio. They are used in aerospace, defense, and electronics applications.
- Catalysis and Polymerization: Alkaline earth metal complexes are used in homogeneous polymerization catalysis. For example, calcium, strontium, and barium can catalyze asymmetric direct-type aldol, Michael, and Mannich reactions.
- High-Energy Materials: They are used in the development of high-energy materials. Their compounds are employed as solid-state precursors and in the initiation of polymerization.
- Electronics and Optoelectronics: Alkaline earth metals are used in the production of semiconductors, particularly in the reduction of impurity incorporation into group-III nitride crystals grown using the ammonothermal method.
- Material Science: Alkaline earth metal oxides are used in the synthesis of organic-inorganic composite films. These films can exhibit enhanced hardness and other material properties depending on the composition.
- Chemical Synthesis: They are used in the synthesis of various coordination compounds, which have applications in chemistry and materials science.
Latest Technical Innovations in Alkaline Earth Metals
Electrophysical Properties and Oxygen Conduction
Recent studies at the Institute of High-Temperature Electrochemistry have explored the electrophysical properties of titanates of alkaline-earth metals doped with acceptor admixtures. These studies highlight the materials’ potential in electrochemical devices, particularly as oxygen-penetrable membranes. The focus is on understanding oxygen-ion, electron, and proton conduction, which are crucial for optimizing their performance in such devices.
Reduction of Impurity Incorporation in Nitride Crystals
They are being utilized to reduce impurity incorporation during the growth of group-III nitride crystals using the ammonothermal method. This innovation aims to improve the purity and quality of these crystals, which are essential for advanced electronic and optoelectronic applications.
Advances in Alkaline Earth-Nitrogen Chemistry
A review on alkaline earth-nitrogen chemistry highlights the diverse synthetic methodologies employed in preparing target compounds. These compounds find applications in polymerization initiation, catalysis, and as solid-state precursors, showcasing the versatility of alkaline earth metals in modern chemistry.
Activated Alkaline Earth Metals for Organometallic Compounds
Innovations in activating alkaline earth metals, particularly magnesium, have led to improved methods for preparing organoalkaline earth metal compounds. This involves the use of activated magnesium forms to enhance the synthesis of Grignard compounds and other organometallics, which are crucial in organic synthesis.
Heavy Alkaline-Earth Metal Organometallic Chemistry
Recent synthetic strategies have overcome the reactivity challenges associated with heavy alkaline-earth metal organometallics, leading to a significant increase in their accessibility. These advancements have expanded their applications, particularly in catalysis and materials science.
To get detailed scientific explanations of the alkaline earth metal, try Patsnap Eureka.

Learn more
Ammonium Hydroxide: A Closer Look at This Ammonia Solution
Pressure Switches: Small Devices, Big Impact
Unveiling The Lead Screw: Its Mechanism, Benefits, And Beyond
